Analyzing Top Armies in the World 2021: The US Footprint
Evaluating the Top Armies In The World 2021 involves considering numerous factors, including troop numbers, technological advancement, budget allocation, and crucially, global reach and power projection capabilities. While a definitive ranking is complex, the United States military consistently features prominently in such analyses due to its unparalleled scale and worldwide presence. The year 2021 marked a significant moment with the conclusion of the 20-year war in Afghanistan, shifting the landscape of US military deployment but not diminishing its vast global infrastructure. This analysis delves into the specifics of the US military’s global posture in 2021, offering insights into the capabilities and reach that positioned it among the world’s leading military forces.
Unrivaled Global Presence: US Military Bases in 2021
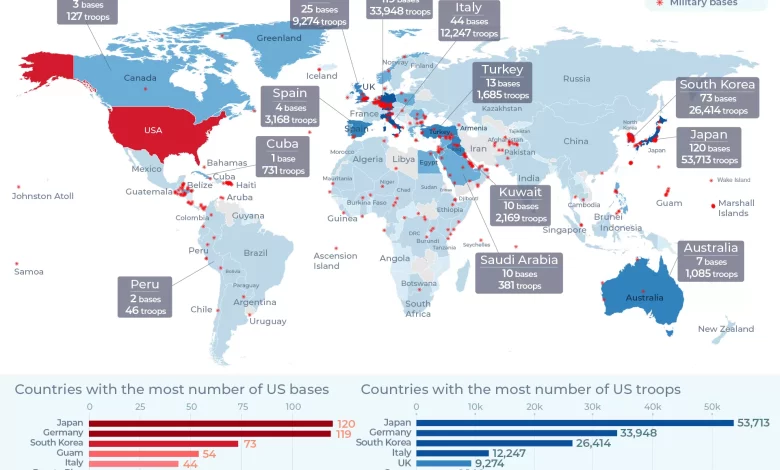
A defining characteristic of the US military’s strength is its extensive network of overseas bases. According to David Vine, a professor at American University, the US operated approximately 750 military bases in at least 80 countries as of July 2021. This number might even be conservative, as the Pentagon does not publicly disclose data on all installations. This vast network facilitates rapid deployment and power projection across the globe.
Japan hosts the highest number of US bases with 120 installations, followed closely by Germany with 119, and South Korea with 73. These bases vary significantly in size and function:
- Large Bases (“Bases”): Defined as military installations exceeding 4 hectares (10 acres) or valued at over $10 million, typically housing more than 200 US military personnel. Around 60 percent (approximately 439) of US foreign bases fell into this category in 2021.
- Small Bases (“Lily Pads”): These are smaller installations, less than 4 hectares (10 acres) or valued under $10 million. They include cooperative security locations and forward operating sites, constituting the remaining 40 percent.

Troop Deployment: A Snapshot of US Forces Abroad
Complementing the extensive base network is the significant number of personnel stationed overseas. As of 2020, data published in the Conflict Management and Peace Science Journal indicated around 173,000 US troops were deployed across 159 countries. Mirroring the base distribution, the countries hosting the largest contingents of US troops were Japan (53,700), Germany (33,900), and South Korea (26,400). These deployments underscore the strategic importance of these alliances and regions to US global military strategy.
Strategic Focus: Key Regions in 2021
The distribution of US forces and bases highlights key areas of strategic interest.
The Middle East: Legacy and Ongoing Operations
The year 2021 saw the end of the direct US military presence in Afghanistan, concluding a 20-year conflict initiated after the 9/11 attacks. The last American soldiers departed Kabul airport on August 31, 2021. At the war’s peak in 2011, roughly 100,000 US troops were stationed there. Despite the withdrawal, US President Joe Biden affirmed the continuation of “over-the-horizon” capabilities, implying air missions launched from regional bases. The largest US military installation in the region remains the Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar, hosting around 11,000 personnel and nearly 100 aircraft. The legacy of interventions in Afghanistan (2001) and Iraq (2003) continues, with around 2,500 US troops remaining in Iraq in 2021 under a security agreement. The human cost, tracked by Brown University’s Costs of War project, estimates 241,000 direct war deaths in Afghanistan alone since 2001, with many more indirect casualties.

Asia-Pacific: Longstanding Alliances
The US has maintained a significant military presence in Japan since the end of World War II and in South Korea since the Korean War. Nearly half of all US troops deployed abroad (around 80,100 personnel) were stationed in these two countries in 2021. Japan hosted 53,700 personnel across 120 bases, while South Korea hosted 26,400 personnel across 73 bases. South Korea is also home to Camp Humphreys, the largest overseas US military base, located strategically south of Seoul and less than 100km from the border with North Korea.

Europe: NATO Commitments and Infrastructure
Europe hosted approximately 60,000 US troops in 2021. Germany had the highest concentration with 33,900 personnel, making it the second-largest host country globally, followed by Italy (12,300) and the United Kingdom (9,300). Notably, US troop levels in Germany decreased significantly from 72,400 in 2006 to 33,900 by 2020. Ramstein Air Base in Germany serves as a crucial logistics hub and is situated near the Landstuhl Regional Medical Center, the largest US military hospital outside the United States, which played a vital role during the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. These bases often function like small cities, equipped with extensive amenities for personnel and their families.

Latin America: The Oldest Overseas Base
The Guantanamo Bay Naval Base in Cuba represents the oldest US overseas military installation. Established at the end of the 19th century and permanently leased in 1903, the 116-square-kilometer facility remains a point of contention between the US and Cuba, which demands its return.

Historical Context: US Deployments Since WWII
The US military’s global presence in 2021 is the result of decades of deployments across more than 200 countries and territories since 1950. Key conflicts shaped this posture:
- Korean War (1950-1953): Following WWII, Korea was divided. The North’s invasion of the South led to US intervention alongside allies. Approximately 1.78 million US troops served, with over 33,000 battle deaths. An armistice, not a peace treaty, ended hostilities.
- Vietnam War (1955-1975): Amid Cold War tensions, the US allied with South Vietnam against the communist North. Over 3.4 million US troops were deployed; the conflict resulted in millions of deaths, including over 58,000 Americans. US combat troops withdrew in 1973.
- Gulf War (1990-1991): After Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait, the US launched Operation Desert Shield, deploying nearly 700,000 troops to the region, leading to a swift coalition victory and ceasefire.
- Post-9/11 Wars (2001-2021): The invasions of Afghanistan (2001) and Iraq (2003) led to massive deployments, with over 800,000 serving in Afghanistan and 1.5 million in Iraq over two decades. The human cost has been immense, with estimates exceeding 900,000 deaths directly linked to these wars.


The withdrawal from Afghanistan in August 2021 was a dramatic visual marker of the end of this era, though the underlying global military infrastructure largely remained.

Financial Might: US Military Spending
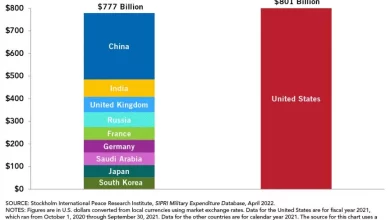
A critical component supporting the US military’s global reach is its substantial budget. In 2020, the US spent $778 billion on its military, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). This figure surpassed the combined military spending of the next ten highest-spending countries. China ranked second at $252 billion, followed by India ($73 billion), Russia ($62 billion), and the UK ($59 billion).

The Costs of War project estimates the US spent $8 trillion on its “global war on terror” over the preceding two decades. The Afghanistan war alone accounted for $2.3 trillion (equivalent to over $300 million daily for 20 years). Iraq and Syria accounted for $2.1 trillion, with other operations costing $355 billion. Significant ongoing costs include over $1 billion in interest payments on war borrowing and $2.2 billion obligated for future veterans’ care. This massive financial investment directly enables the personnel levels, advanced technology, and extensive base network that define US military power.
Conclusion
Determining the absolute Top Armies In The World 2021 requires multifaceted analysis. However, examining the United States military’s posture during that year reveals key attributes of a leading global power: an unparalleled network of approximately 750 overseas bases, significant troop deployments across every major region, sustained historical engagement in global security, and the world’s largest military budget by a substantial margin. The withdrawal from Afghanistan represented a tactical shift, yet the underlying infrastructure enabling “over-the-horizon” operations and rapid global response remained intact. Understanding the scale, scope, and financial backing of the US military footprint in 2021 is essential for comprehending the dynamics of international military power and geopolitical influence during that period.